- contact@vgoshinfo.com
- Mon - Sat: 10.00 am - 7.00 pm
We are creative, ambitious, and ready for challenges! Hire Us
We are creative, ambitious, and ready for challenges! Hire Us
Over 10 years we help companies reach their financial and branding goals. Vgoshinfo is a values-driven technology agency dedicated.
176, Orchard Road, #05-05, The Centrepoint, Singapore 238843
A supply chain has to maintain its competitiveness and match consumer expectations in order to maintain quality control.
End-to-end transparency is provided while the supply chain's flexibility and resilience are increased.
Improving the supply chain gives you control over spending and aids in the elimination of irrational spending in several operational areas.

Increased customer satisfaction and retention rates translate into higher revenue and profitability by enabling you to be quick to act and address any upcoming problems.
Sharing real-time information with your trade partners, such as suppliers, partners, and customers, is made possible by a well-managed supply chain.

Better planning of various supply chain components is made possible by visibility and transparency across the supply chain.

A supply chain is a network that connects a firm with its suppliers in order to manufacture and deliver a certain product to the final consumer. Different activities, people, entities, information, and resources are all part of this network.
The supply chain also depicts the stages involved in getting a product or service from its initial state to its final destination.
The term “value chain” refers to the process by which firms take raw materials, add value to them through production, manufacturing, and other processes to create a finished product, and afterward sell that product to the consumers. The stages involved in getting a product or service to a consumer are called a supply chain, and they frequently involve Original and aftermarket parts.
While a supply chain involves all parties in fulfilling a customer request and leading to customer satisfaction, a value chain is a set of interrelated activities a company uses to create a competitive advantage.
The administration of the movement of goods and services is known as supply chain management, and it encompasses all procedures that transform raw materials into finished items. It entails the deliberate streamlining of a company’s supply-side processes in order to optimize customer value and obtain a competitive edge.
SCM refers to providers’ efforts to design and operate supply chains that are as efficient and cost-effective as possible. Supply chains encompass everything from manufacturing to product creation, as well as the information systems required to coordinate these activities.
There’s more to your supply chain than the sum of its parts. Your success is dependent on the people behind it, including coworkers, suppliers, contractors, partners, and customers. To get there, though, everyone must be on the same page and work for the same company objectives. Today’s supply chains must overcome obstacles such as silos, competing measurements, a lack of visibility, and inadequate communication. Improving communication, having a unified corporate vision, and putting change management methods in place are all critical.
The origins of operations research and industrial engineering in the supply chain industry in Singapore can be traced back to logistics. In his work, industrial engineer Fredrick Taylor, who produced The Principles of Scientific Management in 1911, focused on improving the process of manual loading. Operations During WWII, researchers looked into the value of analytics for logistical military operational solutions. Industrial Engineering and Operations Research have found success by employing integrated frameworks to handle supply chain and logistics difficulties. The term “supply chain engineering” has been coined by the industry to describe this process.
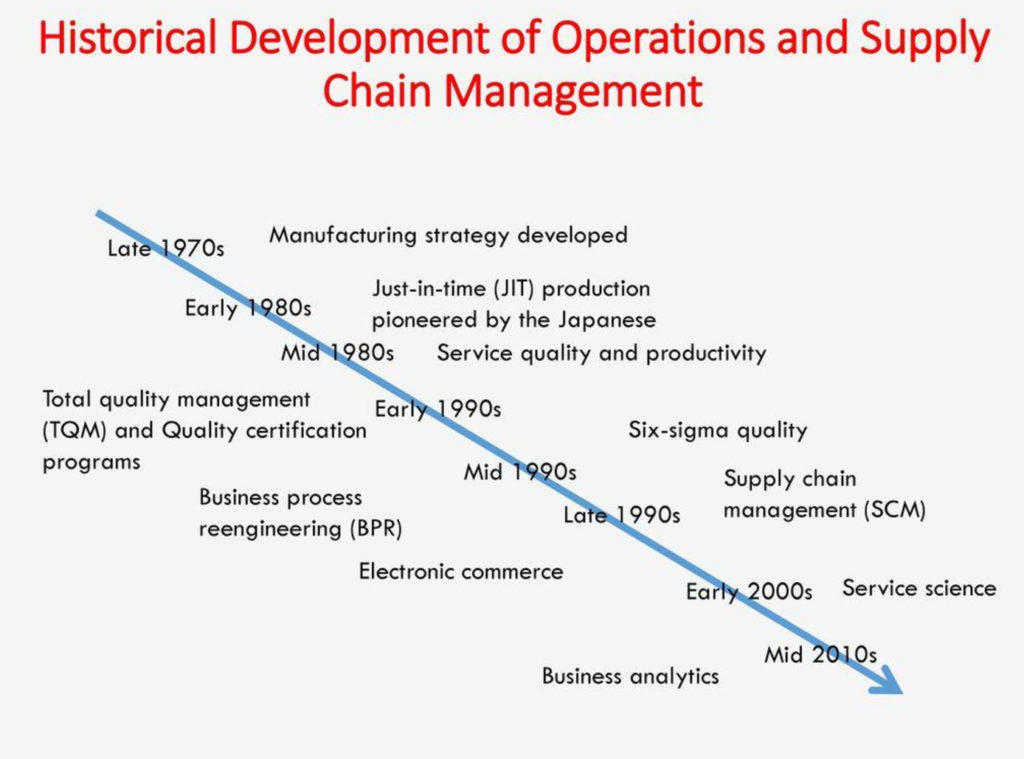
II. Historical Evolution of the Supply Chain
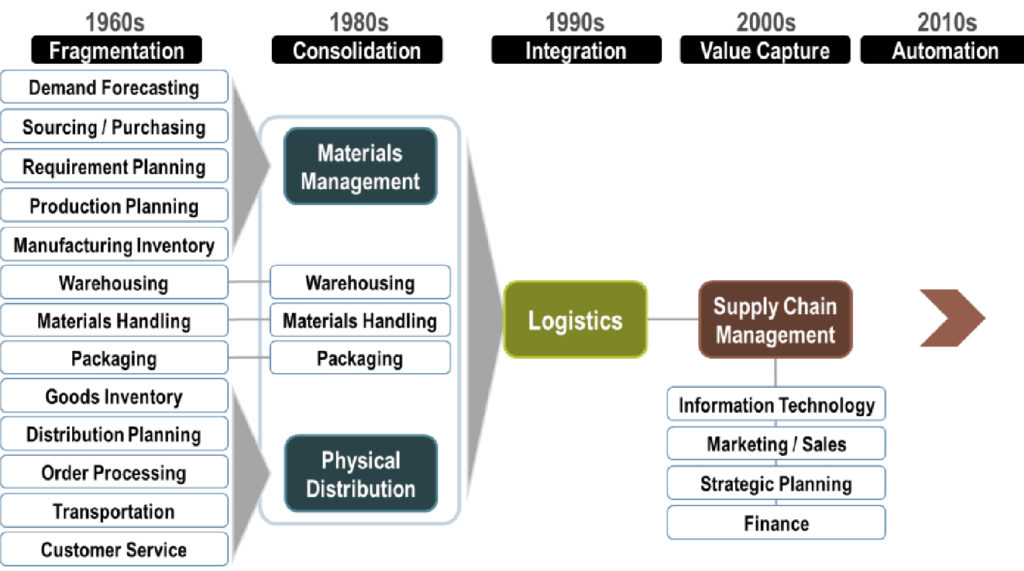
As technologies such as AI become more commonplace in supply chain analytics, companies may see an explosion of further benefits. Information not previously processed because of the limitations of analyzing natural language data can now be analyzed in real-time. The challenge today is how companies can best use the huge amounts of data generated in their supply chain networks. As recently as 2019, a typical supply chain accessed 60 times more data than just five years earlier.¹ However, less than a quarter of this data was being analyzed. Further, while approximately 30 percent of all supply chain data is structured and can be easily analyzed, 70 percent of supply chain data is unstructured or dark data.² Today’s organizations are looking for ways to best analyze this dark data.
Could COVID-19 be the black swan event that finally forces many companies, and entire industries, to rethink and transform their global supply chain model? One fact is beyond doubt: It has already exposed the vulnerabilities of many organizations, especially those who have a high dependence on China to fulfill their need for raw materials or finished products.
China’s dominant role as the “world’s factory” means that any major disruption puts global supply chains at risk. Highlighting this is the fact that more than 200 of the Fortune Global 500 firms have a presence in Wuhan, the highly industrialized province where the outbreak originated, and which has been hardest hit. Companies whose supply chain is reliant on Tier 1 (direct) or Tier 2 (secondary) suppliers in China are likely to experience significant disruption, even if, according to the most optimistic reports, conditions approach normalcy in China by June.
As the COVID-19 threat spreads, here are measures companies can take to protect their supply chain operations:
For companies that operate or have business relationships in China and other impacted countries, steps may include:
For companies that produce, distribute, or source from suppliers in China and other impacted countries, steps may include:
“We have to make decisions with 50% data and the other 50% directed by our purpose and values.” — Supply Chain 50 Member.
Critical to harnessing the universe of supply chain information is an analytics platform that can collect and synthesize data so supply chain leaders can easily:
The Hackett Group’s 2017 Supply Chain Trends study revealed companies unanimously agree that advanced analytics platforms are very important. Based on experience with clients across industries, the following benefits of an advanced analytics program have been identified:
Project inquiries:
60 Paya Lebar Road #07-54 Paya Lebar Square Singapore 409051
Mobile No: +65-8695-8293
2407 Mabolo Garden Flats, Tres Borces St, Cebu, Philippines
Mobile No: +63 927 960 4784
189, Sayee Nagar, 8th St, Virugambakkam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600092
Mobile No: +91-805-684-8685
Vgosh Info LLC, 111 NE, 1st Street, 8th Floor, 88510, Miami, FL 33142
Mobile No: +1 (954)-804-4785
128 City Road,
London, EC1V 2NX
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |